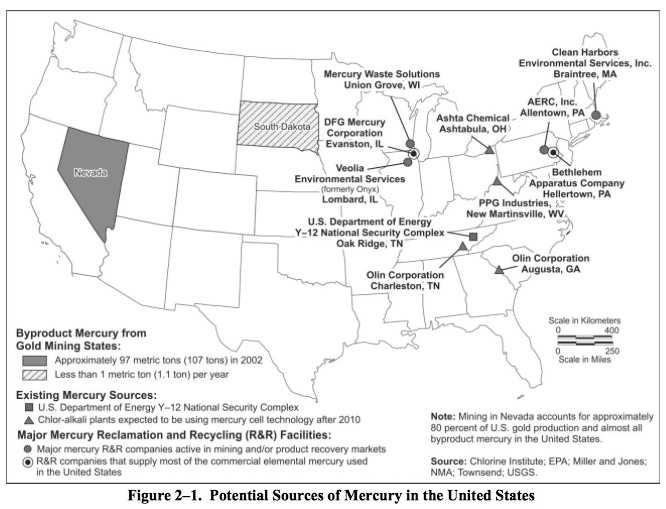
An airport update, comments about mercury storage, and an overview of a proposed 69-kilovolt electrical line for the TRISO-X project at Horizon Center are on the agenda for an Oak Ridge City Council work session on Tuesday.
The rest of this story is available if you are a member: a subscriber, advertiser, or contributor to Oak Ridge Today.
Already a member? Great! Thank you! Sign in here.
Not a member? No problem! Subscribe here:
Basic
- Basic monthly subscription ($5 per month)—access premium content
- Basic annual subscription ($60 per year)—access premium content
Pro
- Pro monthly subscription ($10 per month)—access premium content, get breaking news emails first, and submit one press release or public service announcement per month
- Pro annual subscription ($100 per year)—save $20 per year, access premium content, get breaking news emails first, and submit one press release or public service announcement per month
Temporary
If you prefer to send a check, you may do so by mailing one to:
Oak Ridge Today
P.O. Box 6064
Oak Ridge, TN 37831
We also have advanced subscription options. You can see them here.
We also accept donations. You can donate here. A donation of $50 or more will make you eligible for a subscription.
Thank you for reading Oak Ridge Today. We appreciate your support!