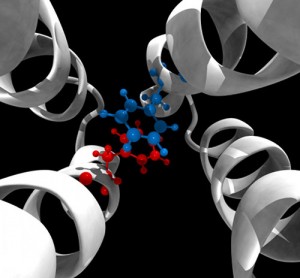
Red and blue molecules represent a conformational switch essential to the signaling mechanism of an E. coli chemoreceptor that researchers discovered using computational molecular dynamics simulations. (Image credit: Davi Ortega)
If scientists can control cellular functions such as movement and development, they can cripple cells and pathogens that are causing disease in the body.
Supported by National Institutes of Health grants, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the University of Tennessee, and the UT-ORNL Joint Institute for Computational Sciences discovered a molecular “switch” in a receptor that controls cell behavior using detailed molecular dynamics simulations on a computer called Anton built by D.E. Shaw Research in New York City. To study an even larger signaling complex surrounding the switch, the team is expanding these simulations on Titan—the nation’s most powerful supercomputer, managed by the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility at ORNL.
Researchers identified the molecular switch on Anton (which was designed to perform speedy molecular dynamics simulations) by simulating 140,000 atoms that make up the signaling part of the Tsr chemoreceptor that controls motility in E. coli. Like other receptors, Tsr spans the cell membrane, communicating to proteins inside the cell in order to respond to threats or opportunities in the environment.
The results, published in Nature Communications, stand apart from previous research because of the computational power applied to the problem.
“This work exemplifies the growing importance of numerical experiments in biology,” said Jerome Baudry, assistant professor in the UT Biochemistry and Cellular and Molecular Biology Department and the UT-ORNL Center for Molecular Biophysics.
The team led by Baudry and Igor Zhulin, distinguished research and development staff member in the ORNL Computer Science and Mathematics Division, joint professor in the UT Department of Microbiology, and JICS joint faculty member determined that a single pair of phenylalanine amino acids called Phe396 located at the chemoreceptor tip was acting as a receptor switch.
“For decades proteins have been viewed as static molecules, and almost everything we know about them comes from static images, such as those produced with X-ray crystallography,” Zhulin said. “But signaling is a dynamic process, which is difficult to fully understand using only snapshots.”
The Phe396 pair is restless, always flipping 180 degrees back and forth relative to the receptor, but researchers identified a clear pattern.
“It is like a crazy light switch,” Zhulin said. “When you switch it on to light up your room, it occasionally flips down giving you moments of darkness, and when you switch it off to go to sleep, it occasionally goes up flashing.”
When the receptor is in signal-on mode, the switch spends more time in the “on” position. When the receptor is in signal-off mode, the switch spends more time in the “off” position.
“To our knowledge, this is the first time this switch has been described,” said Davi Ortega, lead author and postdoctoral fellow in Zhulin’s lab.
The team, including collaborators at the University of Utah led by John Parkinson, compared thousands of chemoreceptor sequences from all microbial genomes in the Microbial Signal Transduction database available as of August 2012. Remarkably, the Phe396 amino acid was present in all of them, indicating it is likely the switch has existed throughout more than two billion years of microbial evolution.
Phenylalanine pairs capable of forming a molecular switch are also present in many other signaling proteins, including receptors in human cells, making it an attractive target for drug design and biotechnology applications.
However, using Anton, researchers were able to simulate only a small part of the chemoreceptor containing the Phe396 pair known as a dimer, meaning two identical molecules. But these two molecules do not work alone.
Dimers are grouped in threes to form larger units of the signaling complex, called trimers of dimers. Researchers expect simulating a trimer next will reveal more about how the Phe396-mediated signal is amplified across neighboring proteins.
But a trimer simulation requires modeling almost 400,000 atoms with increasingly complex physics calculations as the system gets larger. To do so, the group needs a lot of computational capacity.
“Anton is an exceptional machine, but its hardware limitations won’t permit the simulation of such a large system,” Ortega said. “We need Titan.”
Using Titan they ran a preliminary simulation to determine that they would need millions of processing hours on this petaflop machine capable of quadrillions of calculations per second. Titan’s graphic processing units are highly parallel, hurtling through repetitive calculations such as those modeling the large system of atoms under a vast array of configurations in the trimer simulation.
“With Titan we will begin to see how the signal propagates across chemoreceptors,” Zhulin said. “We think this will start to explain how signals are amplified by these remarkable molecular machines.”
Watch the flipping conformations in a pair of phenylalanine amino acids called Phe396 (blue and red molecules), which act as a molecular switch essential to the signaling mechanism of an E. coli chemoreceptor (visualization credit: Davi Ortega):Â www.ornl.gov/File%20Library/Main%20Nav/ORNL/News/Video/molecular_switch_ortega.mpg.
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science. DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit http://science.energy.gov.
Leave a Reply