
ORNL’s Yang Song (seated), Dale Hensley (standing left), and Adam Rondinone examine a carbon nanospike sample with a scanning electron microscope. (Photo by Oak Ridge National Laboratory)
In October, Oak Ridge National Laboratory announced that scientists had developed an electrochemical process that uses tiny spikes of carbon and copper to turn carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into ethanol.
This month, Oak Ridge Today asked if the process using the very small catalysts could be used on a large scale to convert carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into ethanol, and if that might be used to combat climate change.
Here is the response from researcher Adam Rondinone, lead author of a team’s study published in ChemistrySelect:
“If we are successful, then yes, this process will take us a little bit closer to the goal of mitigating climate change. But many other technologies and changes will also be needed, because of the scale of the problem. Also, this technology is more focused on what to do with CO2 (carbon dioxide) once it has been captured. While it could feasibly be coupled to a capture mechanism for extracting CO2 from the air, it will more likely be used to intercept and recycle emissions from point sources like power plants. Ultimately, it will just be one solution out of many that we will need to implement in order to prevent serious climate changes.”
Rondinone said the scientists aim to have the technology ready to license within a year.
“The basic technology is ready, but we’ve decided to try to answer some of the applications-oriented questions like catalyst lifetime and overall energy efficiency in order to shorten the time to commercialization,” Rondinone said. “Oak Ridge National Laboratory has outstanding capabilities and talent who can help us to solve these problems quickly.”
In its October announcement, ORNL said the electrochemical process that uses the tiny spikes of carbon and copper to turn carbon dioxide into ethanol involves nanofabrication and catalysis science, and its discovery was serendipitous.
“We discovered somewhat by accident that this material worked,†Rondinone said. “We were trying to study the first step of a proposed reaction when we realized that the catalyst was doing the entire reaction on its own.â€
The announcement said the team used a catalyst made of carbon, copper, and nitrogen and applied voltage to trigger a complicated chemical reaction that essentially reverses the combustion process. With the help of the nanotechnology-based catalyst that contains multiple reaction sites, the solution of carbon dioxide dissolved in water turned into ethanol with a yield of 63 percent. Typically, this type of electrochemical reaction results in a mix of several different products in small amounts.
“We’re taking carbon dioxide, a waste product of combustion, and we’re pushing that combustion reaction backwards with very high selectivity to a useful fuel,†Rondinone said. “Ethanol was a surprise—it’s extremely difficult to go straight from carbon dioxide to ethanol with a single catalyst.â€
The catalyst’s novelty lies in its nanoscale structure, consisting of copper nanoparticles embedded in carbon spikes, ORNL said. This nano-texturing approach avoids the use of expensive or rare metals such as platinum that limit the economic viability of many catalysts.
“By using common materials, but arranging them with nanotechnology, we figured out how to limit the side reactions and end up with the one thing that we want,†Rondinone said.
The researchers’ initial analysis suggests that the spiky textured surface of the catalysts provides ample reactive sites to facilitate the carbon dioxide-to-ethanol conversion.
“They are like 50-nanometer lightning rods that concentrate electrochemical reactivity at the tip of the spike,†Rondinone said.
Given the technique’s reliance on low-cost materials and an ability to operate at room temperature in water, the researchers believe the approach could be scaled up for industrially relevant applications. For instance, the process could be used to store excess electricity generated from variable power sources such as wind and solar.
“A process like this would allow you to consume extra electricity when it’s available to make and store as ethanol,†Rondinone said. “This could help to balance a grid supplied by intermittent renewable sources.â€
The researchers plan to refine their approach to improve the overall production rate and further study the catalyst’s properties and behavior, ORNL said in the fall.
Besides Rondinone, co-authors of the study are ORNL’s Yang Song, Rui Peng, Dale Hensley, Peter Bonnesen, Liangbo Liang, Zili Wu, Harry Meyer III, Miaofang Chi, Cheng Ma, and Bobby Sumpter. The study is published as “High-Selectivity Electrochemical Conversion of CO2 to Ethanol using a Copper Nanoparticle/N-Doped Graphene Electrode.â€
The work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science and used resources at the ORNL’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, which is a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the DOE’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.energy.gov/.
More information will be added as it becomes available.
See the October announcement here.
Note: Earlier this month, ORNL announced that scientists have found a simple, reliable process to capture carbon dioxide directly from ambient air, offering a new option for carbon capture and storage strategies to combat global warming.
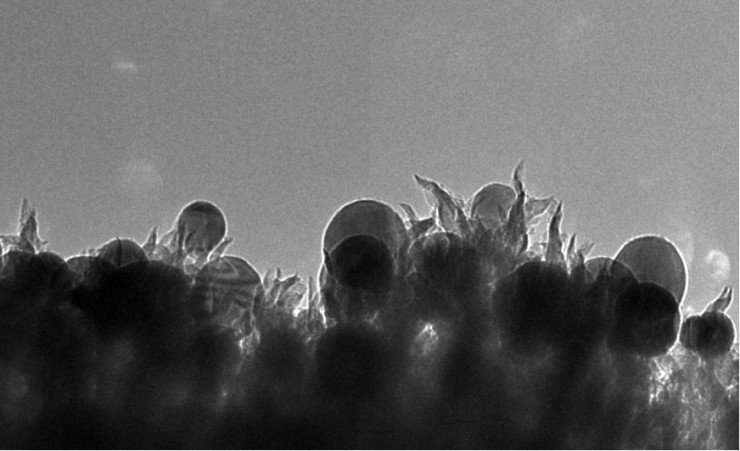
ORNL researchers developed a catalyst made of copper nanoparticles (seen as spheres) embedded in carbon nanospikes that can convert carbon dioxide into ethanol. (Photo by Oak Ridge National Laboratory)
Do you appreciate this story or our work in general? If so, please consider a monthly subscription to Oak Ridge Today. See our Subscribe page here. Thank you for reading Oak Ridge Today.
Copyright 2016 Oak Ridge Today. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed.





Leave a Reply