
A team led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory has identified a novel microbial process that can break down toxic methylmercury in the environment, a discovery that could potentially reduce mercury toxicity levels and support health and risk assessments. Microscopy images by Jeremy Semrau, University of Michigan. (Screenshot from a video by ORNL)
Note: This story was originally published by Oak Ridge National Laboratory on May 31.
A team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has identified a novel microbial process that can break down toxic methylmercury in the environment, a fundamental scientific discovery that could potentially reduce mercury toxicity levels and support health and risk assessments.
Methylmercury is a neurotoxin that forms in nature when mercury interacts with certain microbes living in soil and waterways. It accumulates at varying levels in all fish—particularly large predatory fish such as tuna and swordfish—and, when consumed in large quantities, can potentially cause neurological damage and developmental disorders, especially in children.
A previous ORNL-led study, published in Science in 2013, unlocked the genetic code that led scientists to accurately identify microbes responsible for methylmercury production in the environment. Following this finding, the ORNL team has now discovered which bacteria perform the reverse process, called demethylation. Details are published in Science Advances.
“Much attention has focused on mercury methylation or how methylmercury forms, but few studies to date have examined microbial demethylation, or the breakdown of methylmercury at environmentally relevant conditions,” said Baohua Gu, co-author and a team lead in ORNL’s Mercury Science Focus Area.
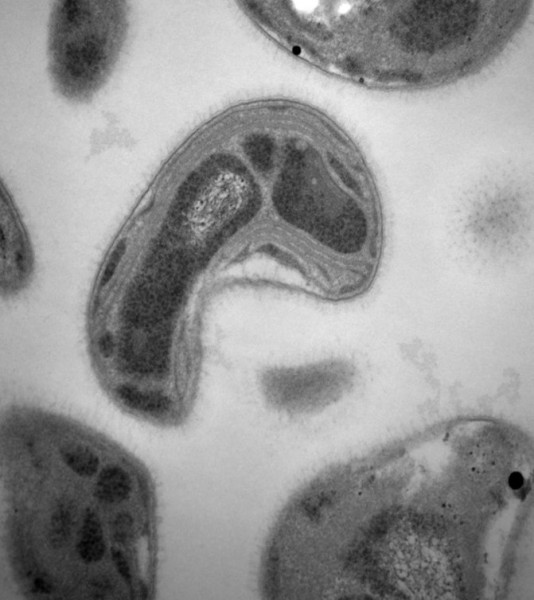
An ORNL-led team along with University of Michigan and Iowa State University investigated many different methanotrophs to single out how and which ones take up and break down methylmercury. (Image by Jeremy Semrau, University of Michigan, via ORNL)
Bacteria called methanotrophs feed off methane gas and can either take up or break down methylmercury, or both. Methanotrophs are widespread in nature and exist near methane and air interfaces, and both methane and methylmercury are usually formed in similar anoxic, or oxygen-deficient, environments.
To single out how and which methanotrophs perform demethylation, the ORNL-led team—along with methanotroph experts from the University of Michigan and Iowa State University—investigated the behavior of many different methanotrophs and used sophisticated mass spectrometry to analyze methylmercury uptake and decomposition by these bacteria. They discovered that methanotrophs such as Methlyosinus trichosporium OB3b can take up and break down methylmercury, while others such as Methylococcus capsulatus Bath only take up methylmercury.
In either case, the bacteria’s interactions can lower mercury toxicity levels in water.
“If proven environmentally significant through future studies, our discovery of methanotrophs’ behavior could be a new biological pathway for degrading methylmercury in nature,” Gu said. This approach differs greatly from a previously recognized enzymatic pathway, which is only effective at very high mercury concentrations.
The methanotrophs identified in this study “open new opportunities to explore how nature detoxifies methylmercury and could improve our prediction of mercury toxicity levels and support better risk assessments and remediation efforts at mercury contamination sites,” Gu added.
Co-authors of the paper titled, “Methylmercury uptake and degradation by methanotrophs,” included ORNL’s Xia Lu, Linduo Zhao, and Baohua Gu; Wenyu Gu, Muhammad Farhan Ul Haque, and Jeremy Semrau of the University of Michigan; and Alan DiSpirito of Iowa State University.
This research was funded by DOE’s Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, as part of the Mercury Science Focus Area at ORNL. ORNL is recognized as a leader for systematic studies of mercury in the environment.
See the ORNL video below:
More information will be added as it becomes available.
Do you appreciate this story or our work in general? If so, please consider a monthly subscription to Oak Ridge Today. See our Subscribe page here. Thank you for reading Oak Ridge Today.
Copyright 2017 Oak Ridge Today. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed.





Leave a Reply